VEX Wrangle Snippets
Views
Actions
Namespaces
Variants
Tools
Translate
Offset the position of geometry
@P += {0, 0.5, 0.75};
Taper
Reduce the circumference gradually from bottom to top
float taper = relbbox(0,@P).y; taper = 1-taper; @P *= set(taper,1,taper);
Boxify
Distorts the geometry into a box shape
vector centroid = getbbox_center(0);
vector size = getbbox_size(0);
size = min(size); // Largest component
@P -= centroid;
@P *= (1.0/size);
@P = lerp(@P, @P+clamp(normalize(@P)*1.75,vector(-1),vector(1)) * (1.0-length(max(abs(@P)))), chf('blend'));
@P *= size;
@P += centroid;
Spherify
Distorts the geometry into a sphere shape
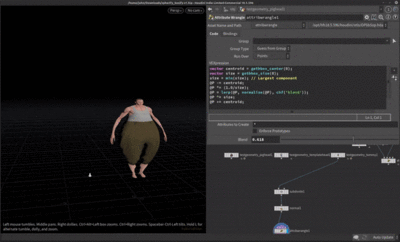
vector centroid = getbbox_center(0);
vector size = getbbox_size(0);
size = min(size); // Largest component
@P -= centroid;
@P *= (1.0/size);
@P = lerp(@P, normalize(@P), chf('blend'));
@P *= size;
@P += centroid;
Stretch
Stretch the geometry across an axis
@P.x += sign(@P.x);
Shape Blending
Blend between two point positions
@P = lerp(@P, @opinput1_P, chf('blend'));
Snap to Grid
Snap (quantize) point positions to a grid for a downres effect
float grid_scale = chf('grid_scale'); // try 8
@P = rint(@P*grid_scale)/grid_scale;
Swizzle Coordinate System
Switch between Y up and Z up coordinates using swizzle
@P = @P.xzy * set(-1,1,1);
Twist
Twirl the geometry around the Y axis
float angle = chf('angle');
vector origin = set(0,0,0);
vector d = v@P*set(1,0,1) - origin;
float r = length(d);
r = pow(r, chf('pow'));
float beta = atan(d.x, d.z) + radians(angle) * r;
v@P = origin + r * set(sin(beta), 0, cos(beta)) + set(0,@P.y,0);
alt
float angle = @P.y*900; vector origin = set(0,0,0); vector d = v@P*set(1,0,1) - origin; float r = length(d); float beta = atan(d.x, d.z) + radians(angle); v@P = origin + r * set(sin(beta), 0, cos(beta)) + set(0,@P.y,0);
alt
float a = chf('angle') * length(@P * {1, 0, 1});
vector pos = @P;
pos.x = (@P.x * cos(a)) - (@P.z * sin(a));
pos.y = @P.y;
pos.z = (@P.x * sin(a)) + (@P.z * cos(a));
@P = pos;
float a = chf('angle') * length(@P * {1, 0, 1});
@P = set( (@P.x * cos(a)) - (@P.z * sin(a)), @P.y, (@P.x * sin(a)) + (@P.z * cos(a)) );
float a = chf('angle') * length(@P * {1, 0, 1});
vector pos = @P;
float u = atan2(pos.x, pos.z);
float r = length(pos * {1, 0, 1});
pos = set(sin(u-a), pos.y, cos(u-a)) * r;
pos.y = @P.y;
@P = pos;
float a = chf('angle') * length(@P * {1, 0, 1});
float u = atan2(@P.x, @P.z);
float r = length(@P * {1, 0, 1});
@P = set(sin(u-a), @P.y, cos(u-a)) * r;
Peak
Moves the mesh along it's surface normals
@P += normalize(@P) * chf('scale');
Exploded View
Moves each packed piece outward from the geometry centroid
@P += (@P - getbbox_center(0)) * chf('scale');
Point Jitter
Jitter each point by a random spherical direction
@P += sample_sphere_uniform(rand(@elemnum+chf('seed'))) * chf('scale');
Plexus Effect
Connect nearby points
foreach(int pt; nearpoints(0, @P, 0.5, 250)) {
if(pt > @ptnum)
addprim(0, 'polyline', @ptnum, pt);
}
Connect to Nearest Point
Draw a line to the closest point of the second input
addprim(0, 'polyline', @ptnum, addpoint(0, vector(point(1,'P',nearpoint(1,@P)))) );
Connect to Closest Surface Position
Draw a line to the closest surface position
addprim(0, 'polyline', @ptnum, addpoint(0, minpos(1,@P) );
Randomize the Rotation of Packed Primitives
Update the transform intrinsic to a random orientation
vector r = sample_direction_uniform(rand(@primnum)); matrix3 x = primintrinsic(0,'transform',i@primnum); rotate(x, PI*pow(rand(@primnum-666),0.5), r); setprimintrinsic(0,'transform',i@primnum,x);
Randomize the Scale of Packed Primitives
Update the transform intrinsic to a apply a random scale
vector s = rand(i@primnum); s = s.yyy; // Uniform Scale matrix3 x = primintrinsic(0,'transform',i@primnum); scale(x, s); setprimintrinsic(0,'transform',i@primnum,x);
Random Color from Normal Direction
Generate random colors based on the surface normal, adjust the multiplier to control the amount of colors
v@Cd = rand(rint(v@N*8));
Iterative Face Insetting
Recursive divide and inset edges, via @d_gfx, excellent use of arrays
int pts[] = primpoints(0,@primnum); vector pos[];
int edge_div_pts[]; vector edge_div_pos[];
foreach( int pt; pts )
append(pos, vector(point(0,'P',pt)));
for( int i = 0; i < chi('iterations'); i++ ) {
resize(edge_div_pts,0); // empty
resize(edge_div_pos,0); // empty
for( int j = 0; j < len(pts); j++ ) {
append(edge_div_pos, lerp( pos[j], pos[(j+1)%len(pts)], chf('div_ratio') ));
append(edge_div_pts, addpoint(0, edge_div_pos[-1])); // [-1] grabs the last item from an array
}
for (int k = 0; k < len(pts); k++ ) {
addprim(0, 'poly', pts[k], edge_div_pts[k], edge_div_pts[(k+2)%len(pts)]);
}
pts = edge_div_pts;
pos = edge_div_pos;
}
addprim(0, 'poly', edge_div_pts);
removeprim(0,@primnum,1); // Remove the input prim and any points belonging to it
Iridescent Color Function
Produce an iridescent color ramp from any varying value, from shadertoy
float amt = dot(@N, set(0,1,0))*0.5+0.5; v@Cd = (0.5 + 0.5 * cos( PI*2*( amt + set(0,1,2)/3) ) );
Rainbow Colors from HSV Colorspace
You can easily control the hue, while keeping the saturation and value the same using the hsvtorgb function.
This allows you to easily create rainbows, gradients, perform hue rotations and produce complimentary colors.
vex_hsvtorgb_rainbow_001.hiplc
v@Cd = hsvtorgb( set(relbbox(0,@P).z - @Time/5 + dot(@N,set(0,1,0))/2, 1, 1));
Loop Over All Attributes
string pt_attrs[] = detailintrinsic(1,'pointattributes');
foreach( string pt_attr; pt_attrs ) {
if( pt_attr ~= 'attr_name*' ) {
setpointgroup(0, pt_attr, @ptnum, 1);
}
}
Remove Faces Across Bounding Box
if( relbbox(0,@P).x < rand(@primnum) )
removeprim(0,@primnum,1);
Torus Knot
float u = float(@ptnum)/(@numpt-1); u += @Time/10.0; u %= 1.0; u *= PI * 2; float r = 2.0; float q = 2; float p = 3; f@u = u; @P.x += cos(u*q) * (cos(u*p)+r); @P.y += sin(u*q) * (cos(u*p)+r); @P.z += sin(u*p);
Make a Quad
int prim = addprim(0,'poly'); addvertex(0,prim,addpoint(0,set(0,0,0)) ); addvertex(0,prim,addpoint(0,set(1,0,0)) ); addvertex(0,prim,addpoint(0,set(1,0,1)) ); addvertex(0,prim,addpoint(0,set(0,0,1)) );
Make a Circle
This example shows how you can generate a circle or N sided polygon using a for loop, sin and cos.
Run the code in detail mode with an attribute wrangle.
This is essentially the same idea as the circle node but hopefully a beneficial example to see how this type of geometry is generated via VEX.
int prim = addprim(0,'poly');
int seg = chi('segments');
for( int i = 0; i<seg; i++ ) {
float u = float(i)/seg * 2*PI;
addvertex(0, prim, addpoint(0, set(sin(u),0,cos(u))) );
}
Groups to Attribute
//convert numbered groups to a numbered attribute
string groups[] = detailintrinsic(0, "primitivegroups");
int prim = @primnum;
string elemnum;
foreach(string i; groups)
{
//if the current primitive is in group i
if(inprimgroup(0,i,prim) == 1)
{
elemnum = re_find(r"\d{3,6}",i);
}
}
s@number = elemnum;
Looping Curl Noise
It's possible to achieve seamless looping animation from curl noise by blending between two noises.
In this example one noise is calculated at the current time, and a second noise is calculated with the time shifted back by the desired loop duration. These two noises are blended from the first to the second over this duration.
// Position x Frequency vector p = @P*0.5; // Speed float s = 0.5; // Loop Length (in seconds) float l = 5; // Time % duration float t = (@Time%l); // Blending vector v0 = curlgxnoise(p + set(0,0,0,t*s)); vector v1 = curlgxnoise(p + set(0,0,0,(t-l)*s)); @P += lerp(v0,v1,frac(@Time/l)) * 0.35;